The classification of high blood pressure is a system that is used to assess the gravity and the stage of the development of high blood pressure.
Attention!In the international classification of diseases of the tenth revision (CIM-10), high blood pressure of inorganic nature is indicated by code I10.
Hypertonic disease: definition, description and etiology
About 50% of people suffer from hypertension (GB).About half of hypertension does not know what suffers from the disease.More than 50% of patients with known hypertension are not treated or ineffective drugs are received.The main cause of the mortality of adult hypertension patients is brain or heart infarction.

The prevalence of high blood pressure increases with age and body weight.Men at a young age often suffer from illness that women.Women in post-menopause suffer more often from hypertension than men.
High blood pressure can be divided into primary (essential) and secondary (organic).
The vast majority (> 90%) of hypertension has primary hypertension, defined as idiopathic.Primary hypertension is diagnosed by excluding organic pathologies.
Some risk factors may increase the risk of developing the disease at early age.In medicine, modified and not modified factors of the formation of the disease are distinguished.These include:
- Obesity;
- Excess salt, alcohol in a diet;
- Smoke cohabitants (they represent a danger, because the patient involuntarily becomes a passive smoker);
- Stress;
- Hypodynamia (lack of sport in the life of the patient);
- Smoking;
- Circulatory disorders (in a small or large circle);
- Age of the elderly;
- Weak social status.
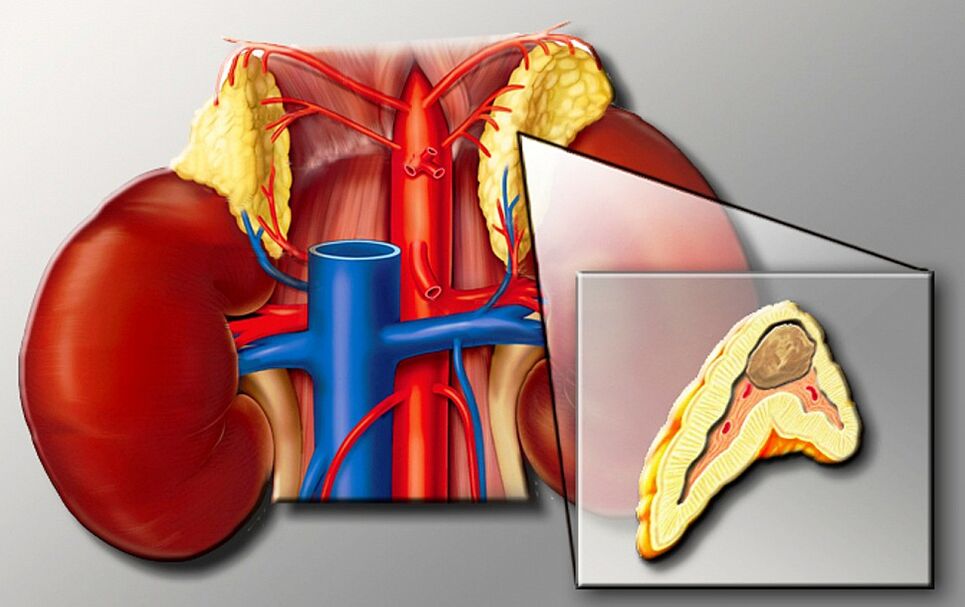
Secondary hypertension (symptomatic) is due to another disease - apnea syndrome in a dream, aortic coarment or aortic sclerosis.Neurogenic, psychogenic and podogenic forms are also known.The last form includes, among other things, ovulation inhibitors and NSAIDs.Drugs and toxic substances, as well as very high liquorice consumption can lead to a secondary form of hypertension.The renal hypertension caused by the stenosis of the renal artery, as well as hyperaldosteronism, pheochromocytoma, kushying disease or hyperthyroidism belong to the secondary forms of hypertension.
Another type of high blood pressure occurs with a hypertensive pregnancy disorder (GEC).Risk factors include mother's high age and multiple pregnancy.Various forms are known, including, for example, gestational hypertension with or without proteinuria.
Pathophysiology
High blood pressure occurs due to an increase in peripheral resistance, an increase in cardiac flow or combinations of both.There are several adaptation mechanisms in this process, so blood pressure is constantly maintained at an increased level.To maintain a heart ejection, the heart becomes hypertrophied and can withstand a constant pressure load.
The kidneys also play an important role in the pathogenesis of hypertension.Although the renal blood flow and the glomerular filtration rate remains largely constant, the excretion of sodium also increases.The influence, for example, of the secretion of renin or the modified reabsorption of sodium on pressure, is discussed.
Symptoms
Often, symptoms of high blood pressure are too late.In most cases, the disease is asymptomatic.
Hypertension can be characterized by the following symptoms:
- Pain early in the head in the head;
- Sleep disturbances, dizziness;
- Epistaxis;
- Tinnitus;
- Non -specific cardiac disorders;
- Tremblant of the atrial.
In the case of secondary hypertension, symptoms of the underlying disease are added.Special hypertension forms are hidden hypertension (SG) and white dresses syndrome (SBC).
With SBC, blood pressure increases ≥ 140/90 mm Hg. Art.When the doctor's office is measured.At home and when monitoring blood pressure, normal blood pressure values are recorded.
With hidden hypertension, the doctor's blood pressure values are in the normal beach.Home measurements or blood pressure monitoring show increased values of ≥ 140/90 mm Hg. Art.This form can be associated with factors such as male sex and younger age, as well as smoking, alcohol consumption and stress.
With a hypertensive crisis, it is necessary to prescribe the correct treatment regime in order to prevent pathological processes in the organs.Patients with this disease should cause emergency aid or take it to the clinic by themselves.Lack of treatment can threaten the patient's life and cause irreversible consequences.The progression of blood pressure can be malignant, which will cause an unjustified risk.If vascular symptoms occur, it is recommended to see a doctor immediately, as a crisis can cause disability for life.
Classification of hypertension by diploma
The stages of high blood pressure have been distinguished by one who.An increase in blood pressure, which occurs, for example, after physical stress, is not considered hypertension.
A low -load disproportionate blood pressure level is called labile hypertension.The dangerous form of high blood pressure is associated with diastolic blood pressure greater than 120 mm Hg. Art., Which decreases by less than 10% during the night.
NEW (2017) Classification of hypertension in stages and degrees: the table is given below.
| AG stages | Systolic pressure in MM Hg. Art. | Diastolic pressure in MM Hg. Art. |
|---|---|---|
| Optimal | <120 | <75 |
| Normal | 120-125 | 75-79 |
| Normal | 126-129 | 80-85 |
| 1st step: start of hypertension | 130-150 | 85-99 |
| Step 2: moderate hypertension | 160-179 | 100-109 |
| Step 3: severe hypertension | ≥ 180 | ≥110 |
| Isolated systolic hypertension | ≥130 | <90 |
Classification of high blood pressure by diploma
Hypertension can be classified according to damage to blood vessels, eyes, heart, kidneys.In accordance with WHO recommendations, there are 3 degrees of hypertension.In the first degree, there is no clinical sign of damage to organs.In the second degree, target organs are affected and vessel atherosclerosis is detected.With the third degree, obvious cardiovascular complications arise from the toad, a heart and cerebral heart attack, transient ischemic attacks.
Risk stratification with pronounced high blood pressure determines the probability of complications.Depending on the high blood pressure stage, the risk may vary considerably.
Important!Only a doctor can determine the correct diagnosis, the risk category, to give certain types of recommendations for prevention and treatment.It is not recommended to independently calculate the risk on undelicated scales and to try to treat the disease.The treatment of a child and a teenager may differ.A variety of treatments is chosen by a doctor on the basis of medical history.
Complications
The problem of high blood pressure is that it is often not diagnosed for a long time or is poorly treated.The absence of symptoms forces patients not to ask for a doctor.This leads to complications that often appear in the heart, kidneys, central nervous systems and eyes or in the vessels of the lower limbs.Often, pronounced atherosclerosis develops.
Hearts and insufficiency, as well as coronary diseases, are important consequences of hypertension of the heart.The heart increases to withstand an increased load.The result is a levage failure.
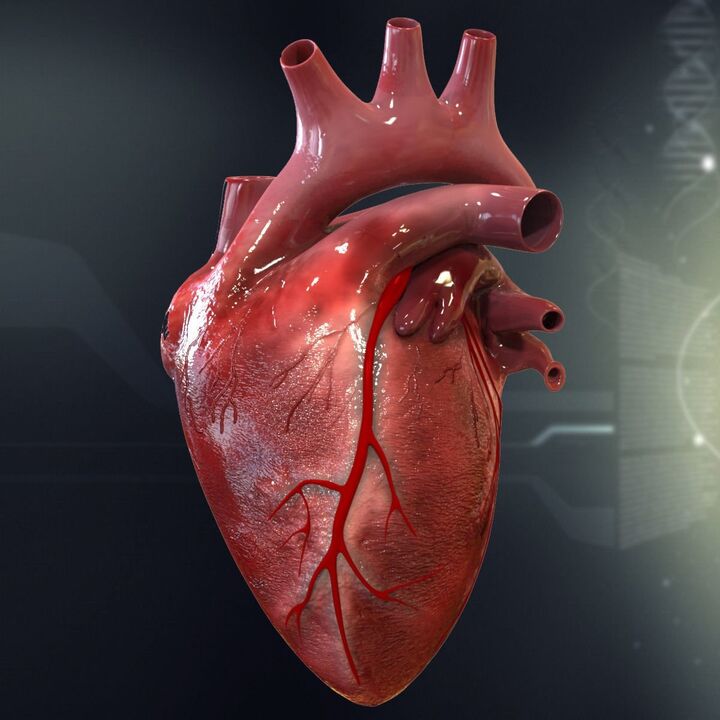
Following atherosclerotic changes in the coronary arteries, the coronary reserve is so limited that even a slight increase in cardiac speed during stress can cause angina, myocardial infarction or sudden coronary death.
Hypertonic nephropathy - kidney damage due to hypertension.It can occur following endothelial damage.Years of exposure to high blood pressure can cause pronounced nephrosclerosis with renal failure of the last step.
The GA can cause transient ischemic attacks (TIA), a brain heart attack, hypertonic mass bleeding or acute encephalopathy.The risk of stroke can be considerably reduced by antihypertensive treatment.
Hypertonic retinopathy, as a rule, occurs following the spread of atherosclerosis in the blood vessels of the retina.Vascular diseases caused by hypertension are OZPA, aneurysm of the abdominal aorta and aortic dissection.
Treatment method
The treatment of hypertension begins with a non -drug intervention.The main non -drug therapy methods for the disease:
- A decrease in body weight to 25 units according to BMI;
- Transition vers un régime à faible sel de <5 à 6 g de NaCl par jour (il est recommandé de sélectionner un régime de tableau de bord);
- Refusal of smoking, alcohol;
- Limit the consumption of caffeine.
It is also necessary to limit the use of hypertensive drugs in the event of hypertension.Patients are recommended to engage in a type of formation from start to back 3-4 times a week, cowardice or bicycle.
In addition to these general measures, it is necessary to treat diseases that cause secondary hypertension.According to the European Hypertension Association, the target blood pressure values should be> 140/90 mm Hg. For patients under 80 years of age and> 150/90 mm Hg. - For elderly patients.
Medicine therapy begins with monotherapy with the drug of choice.To the strongly deflected values of the normal values of blood pressure (> 20/10 mm HG) or the primary combined treatment is carried out with concomitant diseases.
Choice preparations:
- Beta-blockers;
- ACE inhibitors;
- Thiazide diuretics;
- At1 receptor antagonists;
- Long -term calcium blocks.
As a double combination, you can use a diuretic in combination with a beta-blocker, long-term calcium antagonists, ECA inhibitors or AT1 receiver blockers.
Calcium antagonists of the non-hephydropyridine type should not be prescribed with beta-blockers because they contribute to the development of bradycardia or atrioventricular blocking.
According to concomitant disease, individual drugs cannot be prescribed.Diuretics are recommended for hypertension in combination with heart failure.ACE inhibitors can be used for heart failure, as well as in diabetic nephropathy.In the presence of myocardial insufficiency, beta-blockers can also be used.
As for the use of individual drugs, factors such as side effects, individual tolerance and interaction with other drugs that the patient uses.Triple combinations are also possible if a double combination does not provide the desired effect.

















